Some Folks Excel At Joint Genesis And a few Do not - Which One Are You…
페이지 정보
작성자 Taj Barth 작성일23-12-14 05:55 조회6회 댓글0건관련링크
본문
Title: Joint Genesis: Exploring the Mechanisms and Implications of Joint Development in Biological Systems
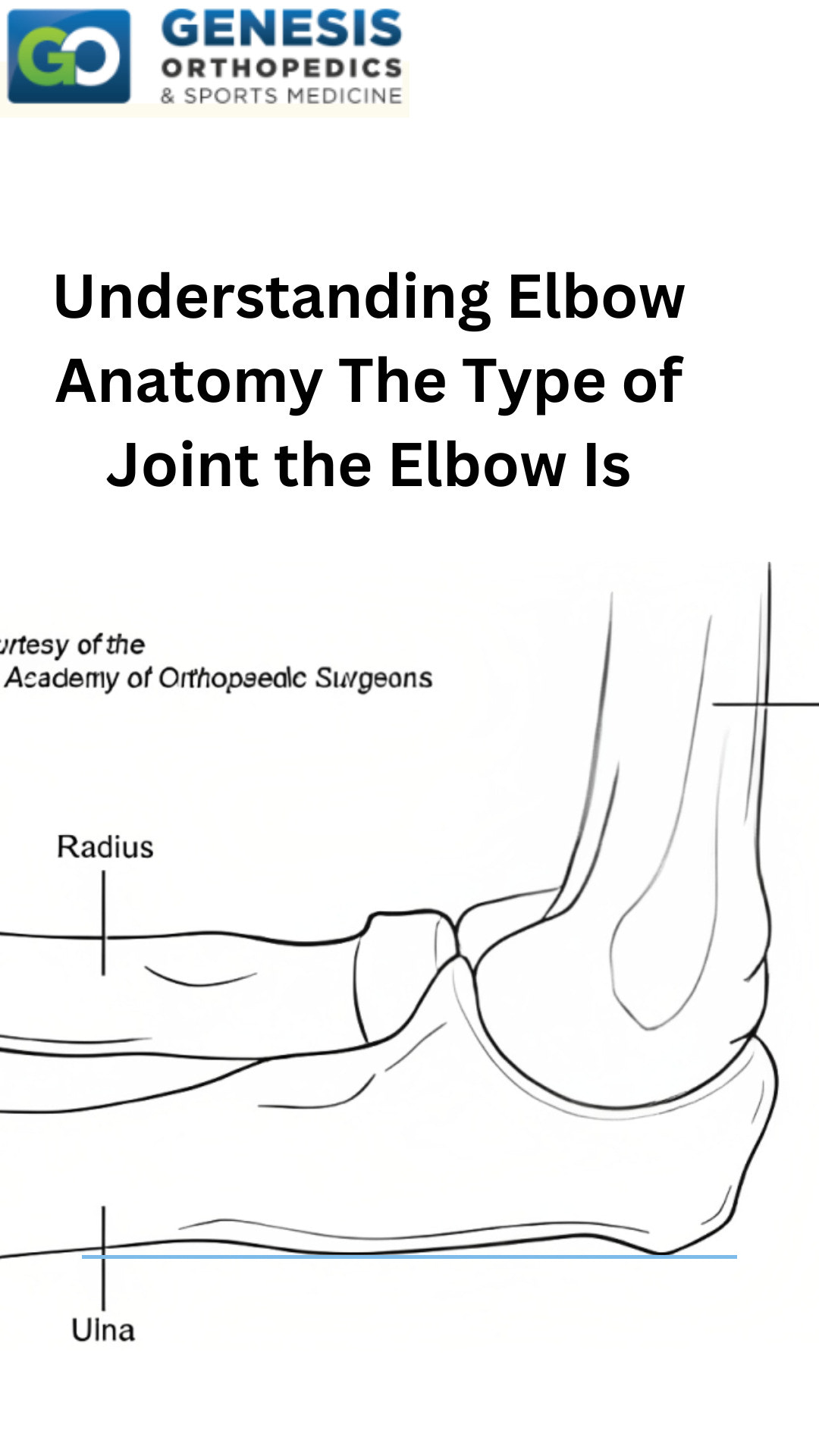 Introduction:
Introduction:
Joint genesis, also known as the development or formation of joints, is a fascinating area of study within the realm of biological systems. Understanding the mechanisms behind joint genesis is crucial for uncovering the complexity of organism development and the implications it carries. This report aims to provide a detailed analysis of current research on joint genesis, including the molecular control, cellular processes, and evolutionary significance.
Molecular Control:
The intricate process of joint genesis involves a series of molecular signals that regulate the formation and patterning of joints. Numerous studies have focused on understanding the role of specific genes and signaling pathways during joint development. Notably, the Wnt and transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) signaling pathways have been identified as key regulators in joint genesis. Wnt signaling is responsible for early joint specification, while TGF-β signaling controls the differentiation and maturation of joint tissues. Insights into these molecular control mechanisms have provided a foundation for further investigation.
Cellular Processes:
Joint genesis involves a orchestration of cellular processes, including cell proliferation, migration, differentiation, and apoptosis. Embryonic progenitor cells in developing joints undergo a complex series of events, leading to the establishment of distinct joint structures. Chondrogenesis, the process of cartilage formation, is a crucial step in joint development, as it provides the necessary framework for joint articulation. Studies have revealed the involvement of various cellular signaling pathways, such as Hedgehog and bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) signaling, in regulating cell fate decisions during joint genesis.
Evolutionary Significance:
The study of joint genesis unveils the evolutionary significance of joint formation in different organisms. Joints represent a hallmark of complex organisms, enabling mobility and adaptability to diverse environments. Comparative studies across species have shed light on the evolutionary conservation of joint development mechanisms, highlighting the underlying genetic and cellular principles that govern joint formation. Insights from these studies have contributed to our understanding of the evolutionary origins of joints and their adaptive significance throughout the animal kingdom.
Clinical Implications:
Understanding the molecular and cellular aspects of joint genesis has significant implications for human health. Joint-related pathologies, such as osteoarthritis and joint dislocations, are prevalent conditions that impact millions of people worldwide. By uncovering the fundamental processes that underlie joint development, researchers can identify potential therapeutic targets for preventing or treating joint disorders. Additionally, advancements in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine are utilizing knowledge gained from joint genesis research to develop novel approaches for joint repair and regeneration.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, joint genesis represents an intricate biological process crucial for the establishment of functional joints in various organisms. Molecular control, cellular processes, evolutionary significance, and clinical implications are all aspects that have been extensively studied within this field. Further investigation into the underlying mechanisms of joint genesis holds the potential to uncover novel therapeutic strategies for joint-related pathologies and deepen our understanding of the complexity of developmental biology.
 Introduction:
Introduction:Joint genesis, also known as the development or formation of joints, is a fascinating area of study within the realm of biological systems. Understanding the mechanisms behind joint genesis is crucial for uncovering the complexity of organism development and the implications it carries. This report aims to provide a detailed analysis of current research on joint genesis, including the molecular control, cellular processes, and evolutionary significance.
Molecular Control:
The intricate process of joint genesis involves a series of molecular signals that regulate the formation and patterning of joints. Numerous studies have focused on understanding the role of specific genes and signaling pathways during joint development. Notably, the Wnt and transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) signaling pathways have been identified as key regulators in joint genesis. Wnt signaling is responsible for early joint specification, while TGF-β signaling controls the differentiation and maturation of joint tissues. Insights into these molecular control mechanisms have provided a foundation for further investigation.
Cellular Processes:
Joint genesis involves a orchestration of cellular processes, including cell proliferation, migration, differentiation, and apoptosis. Embryonic progenitor cells in developing joints undergo a complex series of events, leading to the establishment of distinct joint structures. Chondrogenesis, the process of cartilage formation, is a crucial step in joint development, as it provides the necessary framework for joint articulation. Studies have revealed the involvement of various cellular signaling pathways, such as Hedgehog and bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) signaling, in regulating cell fate decisions during joint genesis.
Evolutionary Significance:
The study of joint genesis unveils the evolutionary significance of joint formation in different organisms. Joints represent a hallmark of complex organisms, enabling mobility and adaptability to diverse environments. Comparative studies across species have shed light on the evolutionary conservation of joint development mechanisms, highlighting the underlying genetic and cellular principles that govern joint formation. Insights from these studies have contributed to our understanding of the evolutionary origins of joints and their adaptive significance throughout the animal kingdom.
Clinical Implications:
Understanding the molecular and cellular aspects of joint genesis has significant implications for human health. Joint-related pathologies, such as osteoarthritis and joint dislocations, are prevalent conditions that impact millions of people worldwide. By uncovering the fundamental processes that underlie joint development, researchers can identify potential therapeutic targets for preventing or treating joint disorders. Additionally, advancements in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine are utilizing knowledge gained from joint genesis research to develop novel approaches for joint repair and regeneration.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, joint genesis represents an intricate biological process crucial for the establishment of functional joints in various organisms. Molecular control, cellular processes, evolutionary significance, and clinical implications are all aspects that have been extensively studied within this field. Further investigation into the underlying mechanisms of joint genesis holds the potential to uncover novel therapeutic strategies for joint-related pathologies and deepen our understanding of the complexity of developmental biology.
댓글목록
등록된 댓글이 없습니다.

